VASCULAR PROCEDURES
Angiogram
Ideal for patients who need to:
- Determine the severity and the location of the narrowing/blockage of blood vessel causing your symptoms
- Initiate treatment for a diseased blood vessel
- locate a bleeding site (often combined with embolisation, which stops the bleeding)
- locate and remove a blood clot in a blocked blood vessel and restore blood flow
- Treat certain types of tumours by blocking their blood supply
- Take blood samples from specific areas to help diagnosis of your condition
- Make a map of your blood vessels before surgery
Benefits:
- Helps diagnose diseases of blood vessels
- Provides information that helps your doctor plan the best treatment for your condition.
- Exact benefits vary between patients.
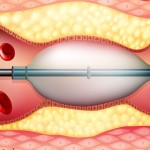
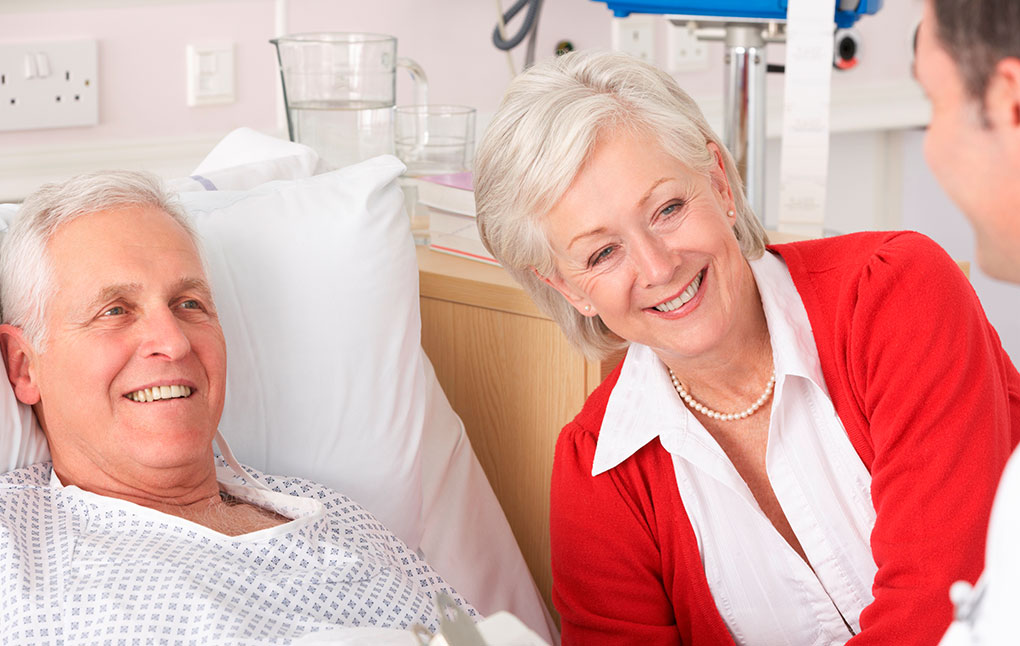
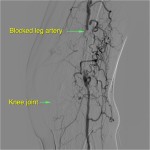
Angioplasty and Stent Insertion of Leg Arteries
Ideal for patients who have narrow or blocked arteries
Benefits:
- Re-open the artery to restore blood flow.
- Walk without pain.
- Allows a wound/ulcer on the leg or foot to heal.
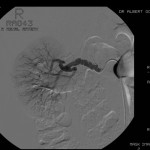
Renal Artery Intervention for Hypertension and End-Stage Renal Disease
Ideal for patients with:
- high blood pressure or hypertension
- symptoms of renovascular disease which include:
– bad taste in the mouth
– chest pain
– confusion or anxiety
– fatigue
– itchy skin
– loss of appetite
– muscle twitching or cramping
– nausea and vomiting
Benefits:
- Improves or stabilises renal function and preserves kidney size.
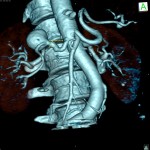
Aneurysms of the Mesenteric, Renal, Splenic Arteries
Mesenteric aneurysm symptoms:
- severe pain in the abdomen occurring within an hour of eating, lasting for 60 to 90 minutes
- weight loss (patients cut back on eating due to the pain)
- diarrhea
- nausea
- vomiting
- flatulence
- constipation
Renal aneurysm symptoms:
- There are usually no symptoms for renal artery aneurysms, and the condition may go unnoticed unless a person is getting imaging for some other reason.
- Can sometimes lead to hypertension.
Splenic aneurysm symptoms:
- Generally there are no symptoms and often diagnosed due to other imaging.
- Some people experience abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting.
- Left untreated, a rupture could be fatal.
Ovarian Vein Embolisation for Pelvic Venous Congestion Syndrome
Ideal for patients with:
- pelvic pain and congestion (particularly women who have had children)
- venous problems in the legs, such as recurrent varicose veins and leg pain related to the menstrual cycle
Benefits:
- Embolisation is a highly effective way of controlling bleeding, especially in an emergency situation.
- Less invasive treatment than conventional open surgery.
- Fewer complications and the hospital stay is relatively short – often only the night after the procedure.
- No obvious surgical incision.
- Can be used to treat tumours and vascular malformations that either cannot be removed surgically or would involve great risk if surgery was attempted.
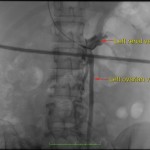
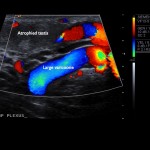
Testicular Varicocoele Embolisation
Ideal for patients with:
- a painful or swollen scrotum
- testicular atrophy (shrinkage)
- fertility problems
Benefits:
- No surgical incision is needed.
- The recovery time is shorter than with open surgery.
- There is a 90% success rate with embolisation.
- Improvement in pain and semen analysis.
- Both sides can be fixed at the same time through one small site.
- Lower rate of complications.
- Low to no risk of infections.
Risks involved in vascular procedures
There are many risk factors that are involved in vascular procedures including a person’s health, lifestyle as well as genetic and environmental factors. One of the most important factors considered by vascular specialists for vascular disease is the age of the patient. Moreover, these risk factors are divided into two categories- one is the accelerators, which are the non-inherited risk factors for a condition and the second is genetic predispositions, which make certain people more susceptible.
Genetic predispositions can influence a person’s strength & structure of blood vessels, blood pressure as well as blood lipid levels. Moreover, it may also increase the risk of diabetes where the body can’t maintain thrombophilia and normal blood glucose level. On the other hand, the accelerators, for vascular diseases are the same as the risk factors for coronary artery disease (also known as heart disease).

