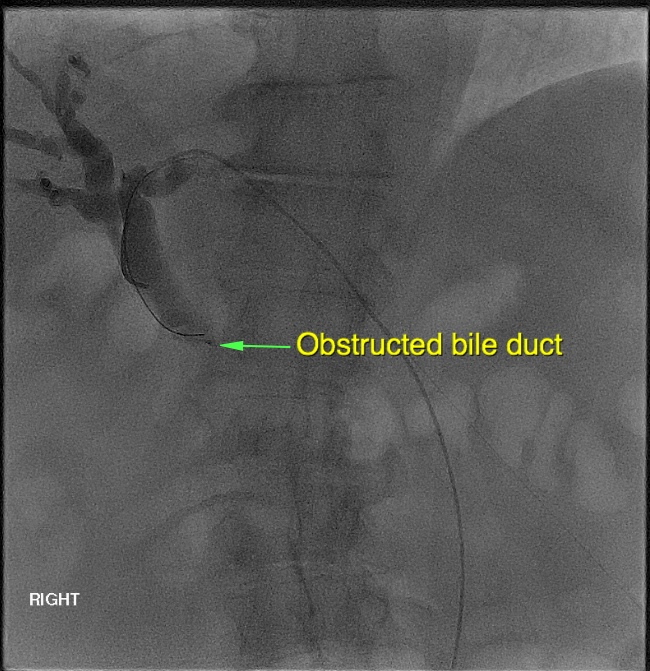
WHAT IS A PTC?
PTC stands for Percutaneous Trans-hepatic Cholangiogram. It is a way of visualising the bile ducts (cholangiogram) by puncturing the skin (percutaneous) and transgressing liver tissue (transhepatic). This form of access to the biliary tree enables minimally invasive intervention such as dilation and stenting of the biliary tree. Dr Goh has been on the faculty of the Annual Hepatobiliary workshop at Royal Prince Alfred Hospital.
WHAT IS BILIARY OBSTRUCTION?
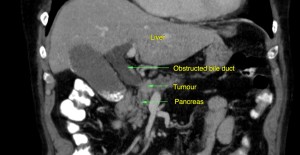
The liver produces bile, which drains into the small bowel. The bile ducts may be obstructed due to problems within the ducts such as stones, strictures or bile duct malignancy. They may also be obstructed due to extrinsic compression from causes such as masses within adjacent organs like the liver, stomach, pancreas or enlarged lymph glands.
HOW IS BILIARY OBSTRUCTION DIAGNOSED?
On initial history and examination, the patient may be jaundiced and blood tests may reveal abnormal liver function and raised bilirubin.
An ultrasound may show dilated bile ducts within the liver which is suggestive of downstream obstruction.
A CT scan may show dilated bile ducts as well as the cause of the obstruction (eg. masses in the liver or surrounding organs).
Finally, contrast may be injected into the biliary tree in order to demonstrate the site of blockage and to potentially treat the obstruction. This may be done endoscopically (ERCP) or percutaneously (PTC).
WHY TREAT BILIARY OBSTRUCTION?
An obstructed biliary tree may lead to problems such as jaundice, liver failure or infection.
HOW IS BILIARY OBSTRUCTION TREATED?
Drainage of the biliary tree may be performed surgically or endoscopically. However, if this is not possible, then the patient will require percutaneous drainage. Initially, a catheter is placed through the skin into the bile ducts using a combination of ultrasound or X-rays. The catheter can then be attached to a drainage bag in order to decompress the biliary tree.

In some cases, a metallic stent is then deployed across the narrowed bile duct in order to hold it open and to restore flow of bile from the liver to the bowel.
Image from PTC after dilation of the bile duct stricture and deployment of a metal stent. The biliary tree is now decompressed and flow to the bowel has been restored.